Switching power supply is an indispensable component of various electronic equipment, and its function is indirectly related to the technical goal of the electronic equipment and whether it can work safely and reliably. Because the internal components of the switching power supply work in the form of high-frequency switching, the power consumption is small, the rate is high, and the volume and weight are only 20%-30% of the power supply, so it has become a tributary product of the regulated power supply. The maintenance of electrical faults of electronic equipment is based on the criteria from easy to difficult. Basically, it starts with the power supply. After confirming that the power supply is normal, other parts of the maintenance are carried out, and power supply faults account for most of the electrical faults of electronic equipment. . Therefore, to understand the basic work principles of the power supply, and to be familiar with its maintenance skills and common faults, it is beneficial to shorten the maintenance time of electronic equipment faults and improve personal equipment technology.
1. No output, general safety tube
This phenomenon affirms that the switching power supply is not working or has entered the form. Firstly, measure whether the startup pin of the power control chip can have a startup voltage. If there is no startup voltage or the startup voltage is too low, check whether the startup resistor and the external components of the startup pin can leak. The above checks can quickly find faults. If there is a startup voltage, measure whether the output terminal of the control chip can have high and low level jumps at the moment of power-on. If there is no jump, declare that the control chip is broken, the peripheral oscillating electrical components or the electricity are defective, and the control can be replaced first. Chip, check the peripheral components; if there is a jump, it is generally a bad or damaged switch tube.
2. Safely burn or fry
Secondly, check the large filter capacitor on the 300V, the diodes of the rectifier bridge, the switch tube and other parts. The problem of anti-interference power will also lead to safety fever and blackening. It should be noted that the safety burning caused by the breakdown of the switch tube will generally burn out the current detection resistor and the power control chip. Negative temperature coefficient thermistors are also easy and safe to burn out all the way.
3. There is output voltage, but the output voltage is too high
This kind of fault generally comes from the steady voltage sampling and steady voltage control of electricity. The DC output, sampling resistor, error sampling amplifier such as TL431, optocoupler, power control chip, etc. form a closed control loop. Any problem will cause the output voltage to rise.
4. The output voltage is too low. In addition to the regulated power supply, it will cause the output voltage to be low. There are also the following reasons that can also cause the output voltage to be low:
A. The switching power supply load has short faults (especially the DC/DC converter is short or malfunctioning, etc.). At this time, all loads of the switching power supply should be disconnected to distinguish whether the switching power supply is faulty or the load power is faulty. If the output voltage is normal when the load is disconnected, the load is too heavy; or the switching power supply is still faulty.
B. The failure of the rectifier diode and filter capacitor at the output voltage side can be judged by substitution method.
C. The performance of the switch tube is reduced, which will inevitably lead to the failure of the switch tube to conduct normally, which increases the internal resistance of the power supply and reduces the load capacity.
Recommended News
Company, Notice, Industry,Exhibition
We and the worldare always changing
![2022 Spring Festival Holiday Notice]() 2022 | 01 | 082022 Spring Festival Holiday Notice2022 Spring Festival Holiday Notice
2022 | 01 | 082022 Spring Festival Holiday Notice2022 Spring Festival Holiday Notice![Thank you for your feedback, thank you! Our company officially issued four denomination vouchers on June 15, 2021]() 2021 | 06 | 15Thank you for your feedback, thank you! Our company officially issued four denomination vouchers on June 15, 2021
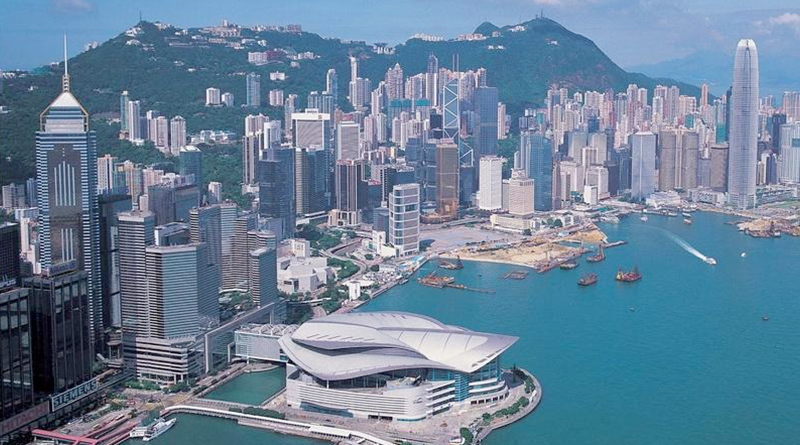
2021 | 06 | 15Thank you for your feedback, thank you! Our company officially issued four denomination vouchers on June 15, 2021![Hong Kong Special Administrative Region International Convention and Exhibition 2022]() 2021 | 05 | 29Hong Kong Special Administrative Region International Convention and Exhibition 2022The Hong Kong International Convention and Exhibition Center is located in the Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Center in Wanchai, Hong Kong. It was established in 1988 and was the second largest conference and exhibition venue in Asia at that time. The Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre is one of the representatives of the newest building complex by the sea in Hong Kong
2021 | 05 | 29Hong Kong Special Administrative Region International Convention and Exhibition 2022The Hong Kong International Convention and Exhibition Center is located in the Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Center in Wanchai, Hong Kong. It was established in 1988 and was the second largest conference and exhibition venue in Asia at that time. The Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre is one of the representatives of the newest building complex by the sea in Hong Kong
 Chinese / 简体中文
Chinese / 简体中文
 English / 英文
English / 英文